Stroke
A stroke or cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is a sudden ‘brain attack’ that occurs when part of the brain loses its blood supply & stops working. This may make it difficult for the person to move their arms and legs, facial muscles to speak and swallow, or to understand what is happening around them.
It can be of ischemic (blockage) or hemorrhagic (internal bleeding) origin. There is another type of stroke called transient ischemic attack (TIA), where the impairment may resolve spontaneously with neurological recovery (reversible ischemic neurological deficit) within a few weeks.
Causes –
A stroke is usually caused by a blood clot blocking part of one of the arteries carrying blood to the brain, or a blood vessel within the brain bursting, resulting in bleeding into the brain.
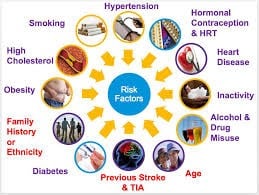
Risk Factors of Stroke:
A family history may increase the risk, as can lifestyle factors such as diet, drinking alcohol, smoking and lack of exercise, but sometimes there is no obvious cause.
• Hypertension
• Diabetes mellitus
• Older age
• Heart diseases
• Obesity
• High cholesterol
Effects of a Stroke –
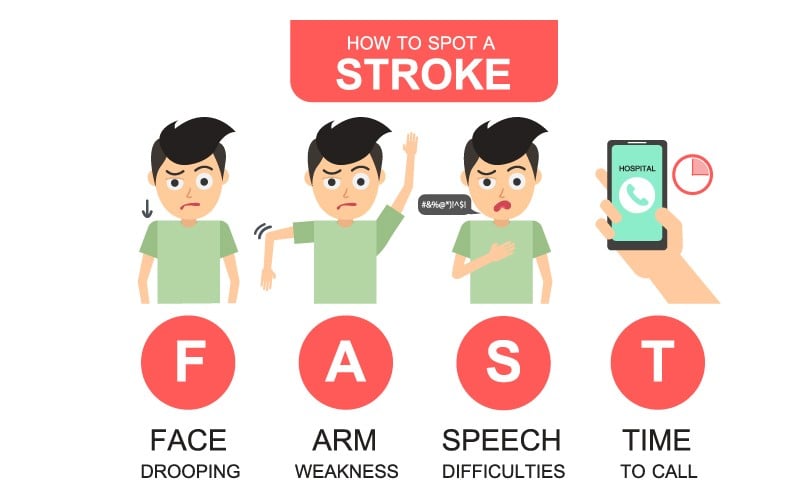
Clinically, the signs and symptoms may vary depending on the area of brain involved, including impairments of motor (movement), sensory (feeling), cognitive, perceptual and language functions. The patients may show signs of paralysis (hemiplegia) or weakness (hemiparesis).
Some common physical effects:
• Reduced mobility
• Weakness or paralysis (usually on one side of the body)
• Reduced sensation
• Neglect to one side of the body
• Swallowing difficulties
• Speech and/or language difficulties
• Incontinence
• Blurred vision
• Fatigue
• Post stroke pain
• Trouble with walking – stumble or have dizziness, loss of balance, loss of co-ordination
Common non-physical effects:
• Mood changes
• Perceptual problems
• Cognitive difficulties
• Behavioural changes
Role of Physiotherapy –
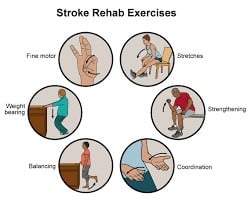
Physiotherapists play a key role in the stroke rehabilitation, as ‘movement expert’. Having a stroke can have a serious impact on movement, sensation, balance and co-ordination and the aim of physiotherapy is to help regain as many of these abilities as possible. The severity of the stroke will dictate how much recovery is possible, but physiotherapy treatment works to maximize movement and mobility to potential recovery.
The recovery of movement is most marked in the first 3 months following a stroke, but progress can still be made many years after a stroke. At Pooja Physiotherapy & Healthcare Centre, we will work with you to help you become as physically independent and fit as possible. Our rehabilitation program is likely to include:
• Daily activities training such as sitting, standing, walking, transfers
• Balance Training Exercise
• Therapy Exercises
• Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) & Bobath concepts
• Manual Therapy such as mobilisation and massage
• Electrical Muscle Stimulation
• Lifestyle modifications
Our therapy program helps –
• Improve balance and walking
• Increase ability to roll / move in bed / sit / stand
• Reduce muscle spasms, pain and stiffness
• Increase & maintain muscle strength
• Retrain normal patterns of movement
• Increase energy levels
• Increase independence and quality of life
• Reduce the risk of falls & other complications
For further information, reach out to us at –
Pooja Physiotherapy & Health Care Center
Blk 77 Indus road #01-521S’160077. Call now @6384 5452 or Whatsapp @8322 3371 or Drop an email at info@physiopoja.com.sg